A) Two π bonds are formed.
B) Two π bonds are broken.
C) Two σ bonds are formed.
D) One π bond is formed.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about elimination reactions is true?
A) Two σ bonds are broken.
B) Two σ bonds are formed.
C) Two π bonds are broken.
D) Two π bonds are formed.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is not true?
A) Two reactions can have identical values for DH° but very different Ea values.
B) The larger the activation energy,the slower the reaction.
C) DH° determines the height of the energy barrier.
D) The lower the activation energy,the faster the reaction.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The conversion of acetyl chloride to methyl acetate occurs via the following two-step mechanism: 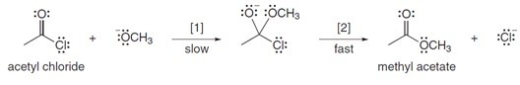 If the concentration of -OCH3 were increased 5 times,what would happen to the rate of the reaction?
If the concentration of -OCH3 were increased 5 times,what would happen to the rate of the reaction?
A) Rate would become one fifth
B) Rate would increase 25 times
C) Rate would increase 5 times
D) Rate would remain unchanged
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following reaction quantities will have an effect on reaction rate?
A) DG°
B) DH°
C) Keq
D) Ea
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is not true?
A) Bond breaking is endothermic.
B) The bond dissociation energy for bond breaking is always negative.
C) Bond making is exothermic.
D) The bond dissociation energy for bond formation is always negative.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which reaction has a positive DG°,assuming that entropy changes are negligible compared to enthalpy changes? 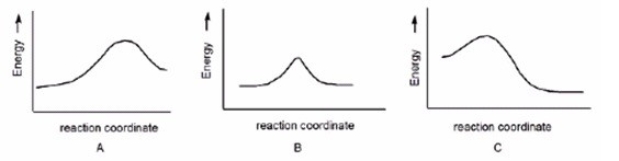
A) A
B) B
C) C
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The DG° (free energy change) for the conversion of A to B is predicted to be which of the following? 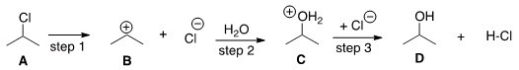
A) DG° = 0
B) DG° < 0
C) DG° > 0
D) Cannot be determined from the information provided
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the name given to the reaction species that lies at an energy minimum between steps on a reaction energy diagram?
A) Transition state
B) Activation energy
C) Reactive intermediate
D) Equilibrium product
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about the equilibrium constant,Keq,is true?
A) When Keq > 1,the equilibrium favors the reactants.
B) When Keq < 1,the equilibrium favors the products.
C) The size of Keq tells about the position of equilibrium.
D) For a reaction to be useful,the equilibrium must favor the reactants.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which compound would you predict to be highest in energy? 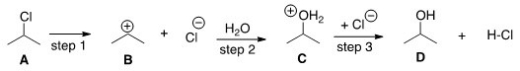
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the Keq corresponds to the lowest value of DG°?
A) Keq = 10-3
B) Keq = 10-2
C) Keq = 10-1
D) DG° cannot be determined.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What kind of reaction does the conversion of A to B represent? 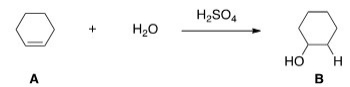
A) Acid-base reaction
B) Elimination reaction
C) Substitution reaction
D) Addition reaction
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the Keq corresponds to the most negative value of DG°?
A) Keq = 1
B) Keq = 101
C) Keq = 102
D) Keq = 103
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Using the bond dissociation energies given,calculate DH° for the following reaction. 
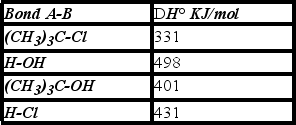
A) +3 KJ/mol
B) -3 KJ/mol
C) -67 KJ/mol
D) +70 KJ/mol
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is not true?
A) In polar reactions,a nucleophile reacts with an electrophile.
B) Carbocations are electrophiles.
C) Carbanions are nucleophiles.
D) A half-headed curved arrow shows the movement of an electron pair.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What type of bond cleavage takes place in/what type of intermediate is produced in the following reaction? 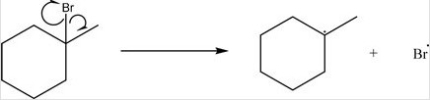
A) Homolysis/Radical
B) Homolysis/Carbocation
C) Heterolysis/Carbocation
D) Heterolysis/Carbanion
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The symbol Δ stands for ________ in a chemical reaction.
A) light
B) heat
C) reactant
D) product
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true?
A) Fast reactions have small rate constants.
B) Slow reactions have large rate constants.
C) A rate equation contains concentration terms for all reactants involved in a one-step mechanism.
D) A rate equation contains concentration terms for all the reactants involved in a multi-step reaction.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which reaction is fast and has Keq = 1? 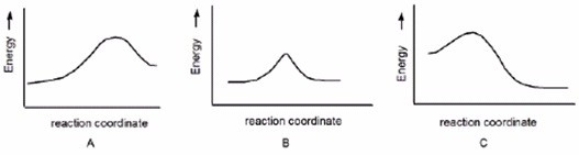
A) A
B) B
C) C
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 53
Related Exams