A) association.
B) perception.
C) projection.
D) integration.
E) localization
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Long-term memory may involve
A) an influx of potassium ions into the neuron.
B) activating substance P.
C) a change in the shape of the neuron's cytoskeleton.
D) forming a nerve plexus.
E) rearranging neurons in the brain.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
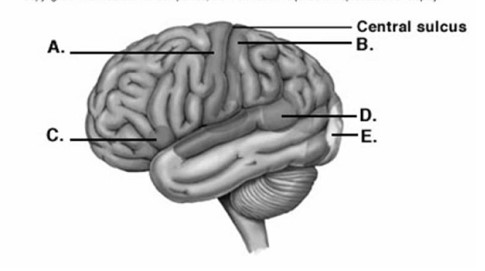 -Label area "E" on the cerebral cortex.
-Label area "E" on the cerebral cortex.
A) visual cortex
B) primary motor cortex
C) primary somatic sensory cortex
D) motor speech area (Broca'sarea)
E) sensory speech area (Wernicke area)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the type of brain wave with its appropriate description. -delta waves C
A) usually occur in children or in adults experiencing frustration
B) observed in a person who is awake,quiet,and resting,with eyes closed
C) occur in deep sleep,infancy and patients with brain disorders
D) occur during intense mental activity
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When people smoke cigarettes,they damage some of their taste buds.Which type of sense has been damaged by the smoking?
A) special
B) somatic
C) visceral
D) autonomic
E) nonspecialized
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is an example of procedural or implicit memory?
A) remembering your name
B) riding a bicycle
C) locating Russia on a globe
D) being afraid of snakes
E) reciting a poem
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following pairs is mismatched?
A) left cerebral hemisphere - analytical hemisphere
B) left cerebral hemisphere - speech area for most of the population
C) right cerebral hemisphere - recognition of faces
D) left cerebral hemisphere - spatial perception
E) left cerebral hemisphere - mathematical hemisphere
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In an ascending pathway,axons of the secondary neuron travel from the
A) receptor to the spinal cord.
B) receptor to the brain.
C) spinal cord through the brainstem to the thalamus.
D) thalamus to the cerebral cortex.
E) spinal cord to cerebellum.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During brain surgery,the superior portion of the primary somatic sensory cortex of a patient is stimulated.The patient is most likely to
A) flex his fingers.
B) talk to the surgeon.
C) smile.
D) feel something touching his back.
E) wiggle his toes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The gate control theory of pain says that pain impulses traveling through the lateral spinothalamic tract can be suppressed by increased activity of the
A) anterior spinothalamic tract.
B) tertiary neurons.
C) extrapyramidal tracts.
D) dorsal column/medial lemniscal system.
E) spinocerebellar tracts.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the kind of pain to the appropriate description. -chronic pain B
A) may occur in amputees
B) migraine headaches are an example of this
C) pain from internal organs sensed in the skin
D) peripheral tissue damage causes increased sensitivity in area of damage
E) increased sensitivity of CNS to tissue damage
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The sensory speech area is Broca area.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In working memory,
A) information is retained for less than a second.
B) the frontal lobe plays the most important role.
C) current information is lost when new information is presented.
D) there is increased synaptic activity by long-term potentiation.
E) there is consolidation of information.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Receptors that in general do not produce an action potential,but can release neurotransmitters in response to a receptor potential are
A) phasic receptors.
B) primary receptors.
C) secondary receptors.
D) tonic receptors.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Procedural memory is stored primarily in the
A) hippocampus and amygdala.
B) central sulcus and Wernicke's area.
C) cerebellum and premotor area of cerebral cortex.
D) temporal lobe and frontal lobe.
E) pons and midbrain.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these combinations of general senses depends on mechanoreceptors?
A) touch and temperature
B) pressure and temperature
C) pressure and proprioception
D) proprioception and temperature
E) taste and smell
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these activities is associated with the right cerebral hemisphere in most people?
A) adding numbers
B) reciting the Gettysburg address
C) painting a watercolor landscape
D) using a calculator
E) making a household budget
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the function with the appropriate structure. -The diagram illustrates sensory nerve endings in the skin.What is the function of "E"?
A) detects deep pressure,vibration,and proprioception
B) responds to painful stimuli
C) responds to light touch and superficial pressure
D) detects touch,involved in 2-point discrimination
E) detects continuous touch or pressure
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If you decide to "snap your fingers," the first neurons to be stimulated are the
A) association neurons.
B) premotor neurons.
C) postmotor neurons.
D) sensory neurons.
E) sensory receptors.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A patient has suffered a cerebral hemorrhage that has damaged the primary motor area of his right cerebral cortex.As a result the
A) patient cannot voluntarily move his right arm or leg.
B) patient feels no sensations on the left side of his body.
C) patient cannot voluntarily move his left eye.
D) patient's heart stops beating.
E) patient cannot voluntarily move his left arm or leg.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 132
Related Exams