A) the forces on it also add up to zero.
B) the object is at rest.
C) the object cannot be turning.
D) the object could be accelerating linearly but it could not be turning.
E) the object could be both turning and accelerating linearly.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A stepladder consists of two halves, hinged at the top, and connected by a tie rod that keeps the two halves from spreading apart. In this particular instance, the two halves are 2.50 m long, the tie rod is connected to the center of each half and is 70.0 cm long. An 800-N person stands 3/5 of the way up the stepladder, as shown in the figure. Neglecting the weight of the ladder, and assuming that the ladder is resting on a smooth floor, what is the tension in the tie rod? Note: To solve this problem you must "cut" the ladder in half and consider the equilibrium of forces and torques acting on each half of the ladder. 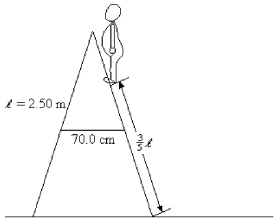
A) 140 N
B) 240 N
C) 280 N
D) 360 N
E) 560 N
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the vector product of 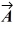 = 2.00
= 2.00  + 3.00
+ 3.00  + 1.00
+ 1.00 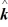 And
And 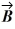 = 1.00
= 1.00  - 3.00
- 3.00  - 2.00
- 2.00 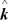 ?
?
A) -3.00 ![]() + 5.00
+ 5.00 ![]() - 9.00
- 9.00 ![]()
B) -5.00 ![]() + 2.00
+ 2.00 ![]() - 6.00
- 6.00 ![]()
C) -9.00 ![]() - 3.00
- 3.00 ![]() - 3.00
- 3.00 ![]()
D) -4.00 ![]() + 3.00
+ 3.00 ![]() - 1.00
- 1.00 ![]()
E) 2.00 ![]() -9.00
-9.00 ![]() - 2.00
- 2.00 ![]()
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A uniform solid sphere has a moment of inertia I about an axis tangent to its surface. What is the moment of inertia of this sphere about an axis through its center?
A) 1/7 I
B) 2/7 I
C) 2/5 I
D) 3/5 I
E) 7/5 I
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A nonuniform, 80.0-g, meterstick balances when the support is placed at the 51.0-cm mark. At what location on the meterstick should a 5.00-g tack be placed so that the stick will balance at the 50.0 cm mark?
A) 16.0 cm
B) 67.0 cm
C) 66.0 cm
D) 35.0 cm
E) 34.0 cm
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At any angular speed, a certain uniform solid sphere of diameter D has half as much rotational kinetic energy as a certain uniform thin-walled hollow sphere of the same diameter when both are spinning about an axis through their centers. If the mass of the solid sphere is M, the mass of the hollow sphere is
A) 3/5 M.
B) 5/3 M.
C) 5/6 M.
D) 6/5 M.
E) 2 M.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A tire is rolling along a road, without slipping, with a velocity v. A piece of tape is attached to the tire. When the tape is opposite the road (at the top of the tire) , its velocity with respect to the road is
A) 2v.
B) v.
C) 1.5v.
D) zero.
E) The velocity depends on the radius of the tire.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the figure, the horizontal lower arm has a mass of 2.8 kg and its center of gravity is 12 cm from the elbow joint pivot. How much force FM must the vertical extensor muscle in the upper arm exert on the lower arm to hold a 7.5 kg shot put? 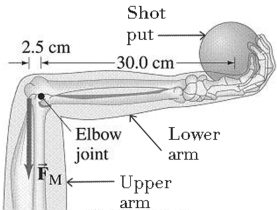
A) 100 N
B) 500 N
C) 750 N
D) 1000 N
E) 1500 N
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A potter's wheel, with rotational inertia 46 kg∙m2, is spinning freely at 40 rpm. The potter drops a lump of clay onto the wheel, where it sticks a distance 1.2 m from the rotational axis. If the subsequent angular speed of the wheel and clay is 32 rpm what is the mass of the clay?
A) 8.0 kg
B) 5.4 kg
C) 7.0 kg
D) 8.8 kg
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The two rotating systems shown in the figure differ only in that the two identical movable masses are positioned at different distances from the axis of rotation. If you release the hanging blocks simultaneously from rest, and if the ropes do not slip, which block lands first? 
A) The block at the left lands first.
B) The block at the right lands first.
C) Both blocks land at the same time.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the figure, a 60-cm length of uniform wire, of 60 g mass and negligible thickness, is bent into a right triangle. The x and y coordinates of the center of mass, in cm, are closest to 
A) (8, 3) .
B) (8, 5) .
C) (9, 4) .
D) (10, 3) .
E) (10, 5) .
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A turntable has a radius of 0.80 m and a moment of inertia of 2.0 kg · m2. The turntable is rotating with an angular velocity of 1.5 rad/s about a vertical axis though its center on frictionless bearings. A very small 0.40-kg ball is projected horizontally toward the turntable axis with a velocity of 3.0 m/s. The ball is caught by a very small and very light cup-shaped mechanism on the rim of the turntable (see figure) . The percent of the initial kinetic energy of the system that is lost during the capture of the ball is closest to 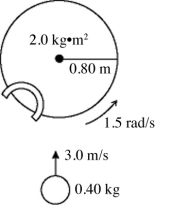
A) 45%.
B) 51%.
C) 55%.
D) 60%.
E) 65%.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A uniform solid sphere is rolling without slipping along a horizontal surface with a speed of 5.50 m/s when it starts up a ramp that makes an angle of 25.0° with the horizontal. What is the speed of the sphere after it has rolled 3.00 m up the ramp, measured along the surface of the ramp?
A) 4.01 m/s
B) 8.02 m/s
C) 1.91 m/s
D) 2.16 m/s
E) 3.53 m/s
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A solid uniform brick is placed on a sheet of wood. When one end of the sheet is raised (see figure) , you observe that the maximum that the angle θ can be without tipping over the brick is 49.6°. There is enough friction to prevent the brick from sliding. What is the width w of the brick? 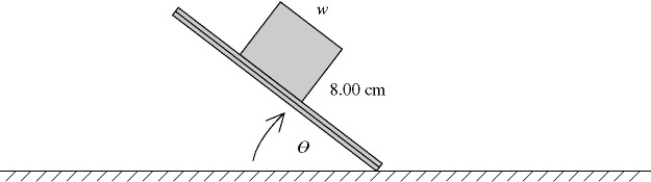
A) 5.18 cm
B) 6.09 cm
C) 6.81 cm
D) 9.40 cm
E) 10.5 cm
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
In the figure, a weightlifter's barbell consists of two identical uniform spherical masses each with radius 0.17 m and mass of 50 kg. The weights are connected by a 0.96-m uniform steel rod with a mass of 12 kg. Find the moment of inertia of the barbell about the axis through the center (see figure). 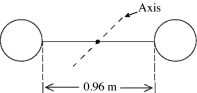
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A uniform solid cylinder of radius R and a thin uniform spherical shell of radius R both roll without slipping. If both objects have the same mass and the same kinetic energy, what is the ratio of the linear speed of the cylinder to the linear speed of the spherical shell?
A) ![]() / 2
/ 2
B) ![]() / 2
/ 2
C) ![]()
D) 4 / ![]()
E) 4 / 3
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A turntable has a radius of 0.80 m and a moment of inertia of 2.0 kg · m2. The turntable is rotating with an angular velocity of 1.5 rad/s about a vertical axis though its center on frictionless bearings. A very small 0.40-kg ball is projected horizontally toward the turntable axis with a velocity of 3.0 m/s. The ball is caught by a very small and very light cup-shaped mechanism on the rim of the turntable (see figure) . What is the angular velocity of the turntable just after the ball is caught? 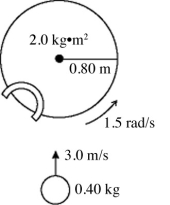
A) 2.1 rad/s
B) 1.3 rad/s
C) 0.94 rad/s
D) 0.75 rad/s
E) 0.30 rad/s
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
There must be equal amounts of mass on both side of the center of mass of an object.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A child is trying to stack two uniform wooden blocks, 12 cm in length, so they will protrude as much as possible over the edge of a table, without tipping over, as shown in the figure. What is the maximum possible overhang distance d? 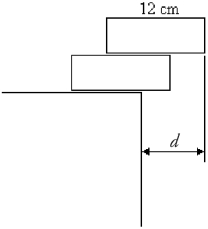
A) 5 cm
B) 6 cm
C) 7 cm
D) 8 cm
E) 9 cm
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the vectors shown in the figure, find the magnitude and direction of the vector product  ×
× 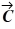 , assuming that the quantities shown are accurate to two significant figures.
, assuming that the quantities shown are accurate to two significant figures. 
A) 16, directed into the plane
B) 16, directed out of the plane
C) 45, directed on the plane
D) 45, directed into the plane
E) 45, directed out of the plane
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 113
Related Exams