A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Choose a structure from the list provided below that best fits the description given. There is only one correct answer for each question. -A reducing monosaccharide
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
F) ![]()
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Draw structures for the products you would expect to obtain from reaction of β-D-galactopyranose with the listed reagents. Be sure to include all relevant stereochemistry. 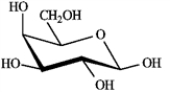 β-D-galactopyranose
-Draw:
Br2, H2O
β-D-galactopyranose
-Draw:
Br2, H2O
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Refer to the sugars below to answer the following question(s). Choose the sugar that best fits each description. There is only one correct answer for each question, but sugars may be used more than once. Indicate each answer by the corresponding letter. -Draw the Fisher projection of L-mannose.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
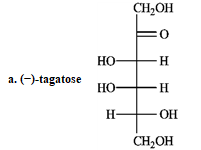
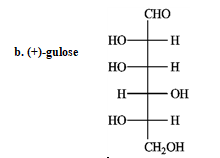
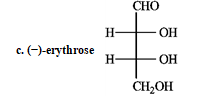
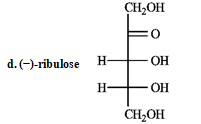
Refer to the sugars below to answer the following question(s) . Choose the sugar that best fits each description. There is only one correct answer for each question, but sugars may be used more than once. Indicate each answer by the corresponding letter. -Refer to instructions. _____ a ketose and _____ an aldose with two chirality centers
A) (-) -tagatose ![]()
B) (+) -gulose ![]()
C) (-) -erythrose ![]()
D) (-) -ribulose ![]()
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Draw an aldopentose with S,S,R stereochemistries at its carbons 2 through 4.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The specific rotation of the pure α-anomer of a monosaccharide is +169.7 and that of the pure β-anomer is +29.4. A solution of the pure α-anomer produces a specific rotation of +61.4. Based on this data, which of the following is correct?
A) The solution contains more of the α-anomer.
B) The solution is an equimolar mixture of the two anomers.
C) A solution of the pure β-anomer would produce the same specific rotation.
D) The change in specific rotation is due to the irreversible formation of the open-chain monosaccharide.
E) All of these.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Treatment with dilute NaOH can convert
A) an aldose into a ketose
B) an aldose into a carboxylic acid
C) an aldose into its acetate ester
D) a glycoside into a monosaccharide plus an alcohol
E) a monosaccharide plus an alcohol into a glycoside
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the sugars below to answer the following question(s) . Choose the sugar that best fits each description. There is only one correct answer for each question, but sugars may be used more than once. Indicate each answer by the corresponding letter. -Refer to instructions. _____ oxidizes to an optically inactive aldaric acid.
A) (-) -tagatose ![]()
B) (+) -gulose ![]()
C) (-) -erythrose ![]()
D) (-) -ribulose ![]()
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the sugars below to answer the following question(s) . Choose the sugar that best fits each description. There is only one correct answer for each question, but sugars may be used more than once. Indicate each answer by the corresponding letter. -Refer to instructions. _____ a dextrorotary hexose and ______ a levorototary tetrose.
A) (-) -tagatose ![]()
B) (+) -gulose ![]()
C) (-) -erythrose ![]()
D) (-) -ribulose ![]()
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following has a D-configuration? 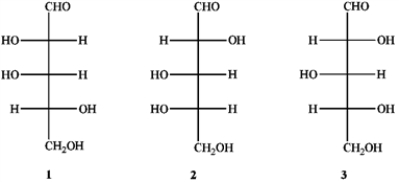
A) only 1 and 2
B) only 1 and 3
C) only 2 and 3
D) only 1, 2 and 3
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Refer to the carbohydrate below to answer the following questions. 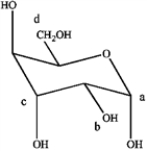 a)Which carbon in the carbohydrate is the anomeric carbon?
b)Does this represent an α or β-anomoer?
a)Which carbon in the carbohydrate is the anomeric carbon?
b)Does this represent an α or β-anomoer?
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Refer to the sugars below to answer the following question(s). Choose the sugar that best fits each description. There is only one correct answer for each question, but sugars may be used more than once. Indicate each answer by the corresponding letter.
 -Complete the equation for the following reaction.
-Complete the equation for the following reaction. 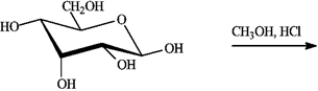
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the sugars below to answer the following question(s) . Choose the sugar that best fits each description. There is only one correct answer for each question, but sugars may be used more than once. Indicate each answer by the corresponding letter.



 -Refer to instructions. _____ a dextrorotary hexose and ______ a levorototary tetrose.
-Refer to instructions. _____ a dextrorotary hexose and ______ a levorototary tetrose.
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Consider the reaction below to answer the following question(s). 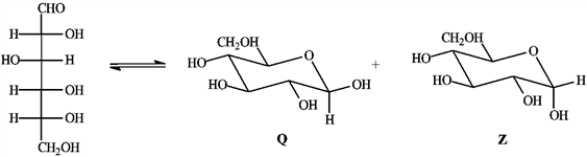 -Refer to instructions. Place a triangle around the anomeric carbon in compound Q.
-Refer to instructions. Place a triangle around the anomeric carbon in compound Q.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the correct structure for α-D-glucopyranose?
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a disaccharide?
A) glucose
B) fructose
C) sucrose
D) N-acetylgalactosamine
E) both c and d
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Draw structures for the products you would expect to obtain from reaction of β-D-galactopyranose with the listed reagents. Be sure to include all relevant stereochemistry.  β-D-galactopyranose
-Draw:
NaBH4 in H2O
β-D-galactopyranose
-Draw:
NaBH4 in H2O
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Refer to the monosaccharides below to answer the following question(s). Classify each sugar by type; for example, glucose is an aldohexose.a. Sorbose 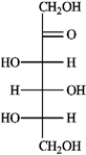 b. Rhamnose
b. Rhamnose 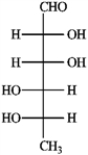 c. Erythrulose
c. Erythrulose 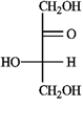 d. Xylulose
d. Xylulose 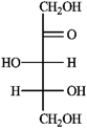 -Refer to instructions. Sorbose is ____________________.
-Refer to instructions. Sorbose is ____________________.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Refer to the monosaccharides below to answer the following question(s).
a. Sorbose 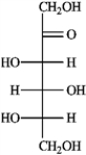 b. Rhamnose
b. Rhamnose 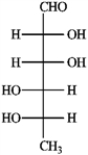 c. Erythrulose
c. Erythrulose 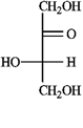 d. Xylulose
d. Xylulose 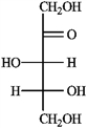 -Refer to instructions. Provide the complete name for the α-anomer of rhamnose in its pyranose form.
-Refer to instructions. Provide the complete name for the α-anomer of rhamnose in its pyranose form.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 49
Related Exams